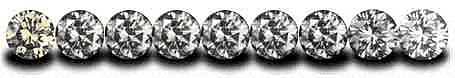|
Definition: Color, when applied to white diamonds, is often misunderstood by people outside the diamond industry. Most people think that all white diamonds are colorless. In fact, truly colorless diamonds are quite rare. The diamonds used most often in jewelry are nearly colorless with faint yellow or brown tints. These diamonds fall into the normal color range. Within the normal color range, the closer to colorless, the more desirable and valuable the diamond. In the 1950's, the GIA introduced the D-Z color grading scale that is still the industry standard. |
 |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
How
is color measured?
Each color grade is actually a narrow range of colors. There is no one exact color for any GIA grade. So, an F-color diamond can be a strong, average or weak F-color. However, as long as the diamond is better than the G-color master, it receives an F-color grade. |
|
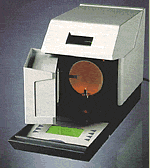
Another way to grade the color of white diamonds is the 'Colorimeter'. It's a dedicated computer that works with a fiber optic light to digitally measure the color of a diamond. The device is 98% - 99% accurate, and is a valuable, unbiased third-party opinion. Although very effective, the color analysis provided by a colorimeter should still be compared to a set of 'master stones'. That's the best way to assure that the diamond's color grade is accurate. |
 |
|
Fluorescence In the 'colorless' range, fluorescence has no effect on color, though it can cause the diamond to have a slightly milky appearance. |
|
Why
is a diamond's color grade important? The less color in the diamond, the more colorful the fire, and the better the diamond's color grade. The better the color grade, the more desirable and valuable the diamond. For example, let's compare the approximate value of 1.0 ct., VS1 clarity, and 'Ideal' cut round diamonds at different color grades:
|
||||||||||||